A large lump on the head can be quite alarming. It often brings with it a flurry of questions and concerns. Many people may contemplate whether it’s the result of a recent bump or something more serious lurking beneath the skin. Grasping the different causes, like head injuries or cysts, is crucial for peace of mind. Each lump tells a unique story, and exploring its origins can lead to effective treatment and reassurance. Let’s uncover what those lumps may signify.
Head Injury
A lump on the head can often provoke anxiety, especially at the time it follows an incident like a fall or a direct hit. This swelling, commonly referred to as a hematoma, is the body’s response to trauma.
Whenever a head injury occurs, blood can collect outside the vessels, causing a firm bump. Bruising might also appear, indicating internal damage. While many minor lumps resolve naturally in one to two weeks, medical evaluation is crucial in the event that symptoms like headaches, dizziness, or unconsciousness arise—these could signal more severe issues.
For most cases, treatment is minimal, allowing the healing process to unfold naturally. Vigilance guarantees peace of mind and safety as the body works through its recovery.
Ingrown Hair and Folliculitis
Ingrown hair and folliculitis are common skin issues that can lead to uncomfortable bumps on the head.
Ingrown hairs occur at times hair grows back into the skin, causing inflammation, while folliculitis involves infection or irritation of hair follicles.
Comprehending their causes and symptoms can help in choosing effective treatment and preventative measures for these bothersome conditions.
Causes of Ingrown Hair
Many individuals experience discomfort from ingrown hairs and the related condition of folliculitis, which can lead to red, painful bumps on the skin.
Comprehending the causes of these conditions can help in finding relief. Some common causes include:
- Shaving Techniques: Improper shaving can result in hairs growing back into the skin, leading to inflammation or infection.
- Tight Clothing: Friction from tight garments can irritate hair follicles, increasing the likelihood of ingrown hairs.
- Poor Hygiene: Insufficient cleanliness can contribute to folliculitis, allowing bacteria or fungi to thrive.
Preventive measures such as practicing good hygiene, using effective shaving techniques, and applying warm compresses can minimize the risk of these bothersome conditions.
For more serious cases, topical antibiotics may be necessary.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
Red, inflamed bumps often signal the presence of folliculitis, a skin condition that can arise from various irritants or infections. Characterized by itching and inflammation, folliculitis can result in pus-filled blisters or crusting. Ingrown hairs, which happen when hair grows back into the skin, often contribute to this condition.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Red Bumps | Inflamed skin around hair follicles |
| Pus-filled Blisters | Forming from infection in follicles |
| Crusting | Occurs as the condition progresses |
In more severe cases, open sores might develop. Areas on the head can be impacted, particularly in cases where tight clothing or poor hygiene practices exacerbate the condition. Awareness of these symptoms is key for effective management.
Treatment and Prevention Tips
The presence of bumps or inflammation on the scalp can be both discomforting and concerning. Effective treatment and prevention strategies for ingrown hairs and folliculitis are key to alleviating discomfort and promoting scalp health.
Consider these helpful tips:
- Maintain Scalp Hygiene: Regularly cleanse the scalp with antibacterial soap to reduce the risk of folliculitis.
- Apply Warm Compresses: Use warm compresses to soothe ingrown hairs and decrease swelling.
- Utilize Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter solutions like hydrocortisone creams can minimize inflammation and itching.
If symptoms, such as increased redness or pus, prevail, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for potential antibiotic treatment.
Practicing proper shaving techniques, like shaving with hair growth, can also help prevent ingrown hairs.
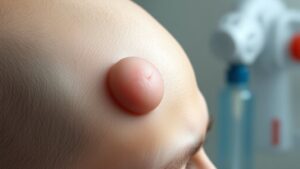
Epidermoid and Pilar Cysts
While residing with a lump on the head can be concerning, comprehending the nature and causes of epidermoid and pilar cysts can provide reassurance.
Epidermoid cysts are non-cancerous lumps that form beneath the skin and contain a thick, yellowish substance called keratin. Pilar cysts, typically found on the scalp, are also keratin-filled sacs that develop from hair follicles.
Most appear smooth, round, and are rarely painful. While they are generally benign, surgical removal could be necessary should they become symptomatic or for cosmetic reasons. This procedure is often an outpatient one and has a low recurrence rate, offering peace of mind to those managing these common and usually harmless conditions.
Lipoma and Pilomatrixoma
After gaining insight into epidermoid and pilar cysts, attention can shift to another duo of common skin growths: lipomas and pilomatrixomas.
1. Lipomas: These benign tumors, made of fatty tissue, are often soft, movable lumps that don’t typically cause pain.
They rarely require treatment unless they lead to discomfort or aesthetic concerns.
2. Pilomatrixomas: Originating from hair follicle cells, pilomatrixomas grow slowly and feel firm.
They often appear on the scalp and could require surgical removal for accurate diagnosis and relief.
3. Medical Evaluation: Despite being non-cancerous, these lumps should be assessed by a healthcare professional when there’s a change in size, shape, or when symptoms develop to guarantee appropriate care.
Skin Cancer and Exostosis
Lumps on the head can raise a lot of questions, especially at the time they’re unfamiliar and concerning. Skin cancer, specifically basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, can manifest as large, persistent lumps, often appearing red, scaly, or bleeding. Meanwhile, exostosis, or bony growths, can develop from chronic irritation or trauma and usually present as hard, immovable masses.
| Skin Cancer Symptoms | Exostosis Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Red, scaly lesions | Hard lumps on the skull |
| Bleeding or crusted areas | Pain or discomfort |
| Changes in mole size/shapes | Non-moving bony growths |
| New growths that don’t heal | Might interfere with surrounding tissues |
| Irregular borders on lumps | Surgical intervention needed should it be painful |
Timely biopsy and treatment, which can include surgical excision, are essential for both conditions.
When to See a Doctor
Not every lump on the head signals immediate alarm; however, certain signs warrant closer attention. Individuals should consider seeking medical attention should they notice a persistent lump on their head that lasts longer than two weeks or grows in size.
Additionally, it is essential to see a doctor should the lump arise after head trauma and is accompanied by confusion, seizures, or unconsciousness.
Here are three key signs that require prompt medical evaluation:
- Redness, warmth, or drainage from the lump could indicate an infection.
- Painful bumps that accompany other symptoms like headaches or dizziness should be scrutinized.
- A hard lump that does not move under the skin could suggest more serious conditions.