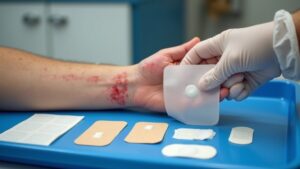
Tegaderm, a transparent adhesive dressing, can sometimes trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Redness, itching, and blisters can develop where the film touches the skin, often due to an allergy to the adhesive or the film itself. Other irritants, like friction or trapped moisture, can worsen the reaction. While these symptoms are usually mild, being aware of how to spot them promptly makes a difference. Luckily, alternatives exist that provide gentle protection for those prone to skin sensitivity.
Signs and Symptoms of a Tegaderm Allergy
Redness, itching, and swelling around the area where Tegaderm is applied are the most common signs of an allergic reaction.
Some people also notice a rash, blistering, or a burning sensation under the adhesive. In rare cases, the skin can peel or develop hives.
These symptoms often appear within hours but can take days to show up. Skin testing can help confirm whether the reaction is due to Tegaderm or another irritant.
Allergy management starts with identifying these signs promptly to prevent worsening discomfort. Removing the dressing and cleaning the area gently can reduce irritation.
Should symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare provider guarantees proper care. Comprehending these reactions aids in making informed choices about wound care alternatives.
Common Causes of Tegaderm Skin Reactions
Tegaderm skin reactions often stem from sensitivity to adhesive ingredients, which can trigger irritation or allergies. Skin barrier disruption, like dryness or minor wounds, makes some people more prone to reactions while using the dressing. Pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or dermatitis, also heighten the risk of discomfort.
—
Tegaderm Allergy Alternatives: Finding Gentle Skincare Solutions
Should you’ve ever had an itchy, red rash after using a Tegaderm dressing, you’re not alone. Many people experience skin reactions to medical adhesives, and it can be frustrating—especially whenever you need a reliable bandage to protect healing skin. The positive update? There are plenty of alternatives and simple ways to reduce irritation while keeping your wounds safe.
Why Tegaderm Causes Skin Reactions
Tegaderm is a transparent film dressing that sticks securely to the skin, but for some, that strong adhesion comes at a cost. The adhesive ingredients, like acrylates or rubber-based compounds, can trigger allergic contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals.
Consider it like a stubborn sticker on sensitive skin—it might cling well but leave behind redness or blisters.
Skin barrier issues also play a role. In case your skin is already dry, cracked, or recovering from minor abrasions, the adhesive can worsen irritation by pulling on delicate tissue. Pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, amplify the problem since inflamed skin reacts more aggressively to foreign substances.
Even friction from movement can rub the dressing against your skin, making small problems worse over time.
Recognizing a Tegaderm Allergy
Reactions vary, but common signs include redness, swelling, or a bumpy rash where the dressing was applied. Some people notice intense itching or even fluid-filled blisters, which could appear hours or days after use.
Unlike typical mild irritation, an allergy often spreads beyond the edges of the bandage and lingers even after removal.
Pay attention to burning or stinging sensations—these are clues your skin isn’t happy. Should symptoms worsen or last longer than a few days, it’s worth checking with a doctor to rule out infection or a severe allergic response.
Gentle Alternatives to Try
For those with adhesive sensitivities, silicone-based dressings are a revolutionary development. They stick securely without aggressive adhesives, making them kinder to reactive skin.
Hypoallergenic options, like those labeled “gentle hold” or “for sensitive skin,” often use milder materials that reduce the risk of rashes.
Non-adhesive dressings, such as gauze secured with paper tape or a loose wrap, work well for minor wounds. Barrier creams or sprays can also help by creating a protective layer between your skin and the adhesive.
Should you be unsure which to pick, pharmacists or wound-care specialists can recommend brands tailored to your skin type.
Easy Steps to Reduce Irritation
Before applying any dressing, clean and dry the area thoroughly—adhesives bond better to oily or sweaty skin, increasing friction. Trimming excess hair (gently!) can prevent tugging, while applying a thin layer of moisture-free barrier film adds extra protection.
Whenever removing the bandage, take it slow. Peeling it off too quickly can aggravate your skin further. Using warm water or oil (like coconut or baby oil) to loosen the adhesive helps minimize discomfort.
Should redness persist, a fragrance-free moisturizer or hydrocortisone cream can calm inflammation.
Whenever to Seek Help
Most mild reactions fade on their own, but persistent pain, spreading rashes, or signs of infection (pus, fever) need medical attention. A dermatologist or allergist can perform patch testing to identify specific adhesive allergies, helping you avoid problematic products in the future.
Skin sensitivity shouldn’t mean sacrificing proper wound care. With the right alternatives and a little extra care, you can protect your skin without the irritation.
Experiment to find what works best for you—sometimes the gentlest solutions are the most effective.
Adhesive Ingredient Sensitivity
While many people rely on adhesive bandages like Tegaderm for wound care, some experience irritation due to the materials used in the adhesive. This sensitivity often stems from ingredients like acrylates, rubber, or latex, which can trigger redness, itching, or even blisters.
To identify the culprit, adhesive testing or skin patching can help pinpoint reactions before full use.
- Acrylate adhesives: Common in medical tapes, these can cause rashes or swelling in sensitive individuals.
- Rubber-based adhesives: Found in some dressings, they might lead to contact dermatitis.
- Latex components: Even trace amounts can provoke allergic responses.
- Preservatives or additives: Chemicals like colophony might irritate over time.
Understanding these triggers guarantees safer choices, especially for those with a history of skin reactions.
Always check labels and consider hypoallergenic alternatives when necessary.
Skin Barrier Disruption Risks
Skin barrier disruption often clarifies why people react to adhesive dressings like Tegaderm, even at times they aren’t allergic to the materials.
Damaged skin struggles to protect foundational layers, making it prone to irritation from adhesives. This happens during wound healing at the time the area is fragile or after prolonged dressing use, which weakens the skin.
Excessive moisture, frequent dressing changes, or harsh removal techniques also compromise the skin barrier, heightening sensitivity. Signs include redness, itching, or a stinging sensation where the adhesive touched the skin.
Keeping the area clean, gently removing dressings, and using skin-friendly alternatives helps prevent further damage. Comprehending this risk guarantees safer care, especially during healing phases while promoting recovery.
Pre-Existing Skin Conditions Impact
- Eczema or dermatitis increases the risk of adhesive-related rashes due to fragile skin.
- Psoriasis flares can worsen as occlusive dressings trap moisture and heat.
- Allergic contact dermatitis can develop should the skin react to Tegaderm’s adhesive components.
- Rosacea or acne-prone skin could become inflamed from prolonged adhesive use.
Understanding these triggers helps in choosing safer alternatives and preventing unnecessary discomfort.
Best Hypoallergenic Tegaderm Alternatives
Several hypoallergenic adhesive options provide gentle alternatives for those sensitive to Tegaderm.
Non-irritating film dressings offer similar protection without causing skin reactions.
These alternatives are specifically designed to be safe for sensitive skin while maintaining effectiveness.
Hypoallergenic Adhesive Options
For those with sensitive skin, finding the right adhesive dressing can feel like a constant battle against irritation.
Hypoallergenic adhesive options minimize reactions through the use of gentler materials, making them ideal for allergy-prone individuals.
These alternatives often avoid harsh chemicals found in traditional medical tapes, reducing redness and itching.
- Natural adhesive materials like silicone or hydrocolloid are less likely to trigger skin reactions.
- Medical tape alternatives such as paper or fabric-based adhesives provide breathability and flexibility.
- Acrylic-free adhesives are a safer choice for those with known sensitivities.
- Hypoallergenic dressings often feature gentle bonding agents that hold securely without damaging delicate skin.
Choosing the right option depends on skin type and the level of adhesion needed.
Testing a small patch initially can help identify the best fit without risking widespread irritation.
Non-Irritating Film Dressings
At the time hypoallergenic adhesive options aren’t quite enough, non-irritating film dressings step in as a strong alternative to Tegaderm for those with sensitive skin.
These dressing materials are designed to minimize irritation while still providing a protective barrier. Made from gentle polymers, they allow the skin to breathe while keeping out bacteria and moisture.
Unlike traditional adhesives, these non irritating options often use softer, medical-grade films that reduce redness and itching. They’re ideal for long-term wear, especially for people prone to reactions.
Some brands even feature silicone-based edges for extra comfort. Since they’re transparent, monitoring wounds is easy without removing the dressing.
For anyone struggling with adhesive allergies, these films offer a reliable, skin-friendly solution that balances protection and comfort.
Safe for Sensitive Skin
Skin that reacts easily needs dressings gentle enough to protect without causing more problems. Hypoallergenic alternatives to Tegaderm reduce irritation, especially for those with delicate skin. Before choosing an alternative wound care product, skin patch testing helps identify safe options.
- Silicone dressings: Soft, non-stick, and less likely to stick to healing skin.
- Hydrocolloid bandages: Absorb fluid while protecting sensitive areas without harsh adhesives.
- Non-adherent gauze: Wrapped with a gentle breathable tape to minimize contact with irritated skin.
- Foam dressings: Cushion wounds while allowing airflow, reducing heat and moisture buildup.
These alternatives prioritize comfort and safety, ensuring protection without triggering reactions. Properly testing materials prevents further discomfort, making recovery smoother.
Choosing the right dressing depends on individual skin needs and wound type.
Silicone-Based Adhesive Dressings for Sensitive Skin
Patients with sensitive skin often struggle with adhesive dressings that cause irritation, redness, or itching.
Silicone-based dressings provide a gentler alternative, as their soft, flexible adhesive minimizes trauma during application and removal. Among the key silicone dressings benefits are reduced sticking to delicate skin, allowing painless repositioning without tearing.
These dressings also create a protective barrier, shielding wounds while letting skin breathe—ideal for sensitive skin solutions. Unlike harsher adhesives, silicone layers conform smoothly to contours, reducing friction and discomfort.
Some options even include soothing gels to calm redness. Since they’re hypoallergenic, they lower the risk of allergic reactions, making them reliable for long-term use.
Lightweight and breathable, these dressings help maintain moisture balance, preventing dryness or maceration around wounds.
Non-Adhesive Wound Covering Options
Several non-adhesive wound coverings offer a comfortable solution for those who experience irritation from traditional bandages.
These options reduce skin contact with adhesives while still protecting wounds.
- Non adhesive gauze: Soft and breathable, it can be secured with a wrap or tape away from the wound. Ideal for minor cuts or burns.
- Hydrocolloid dressing: Forms a gel-like layer over the wound, promoting healing without sticking to the skin. Works well for blisters or ulcers.
- Foam dressings: Absorbent and cushioning, they’re gentle on sensitive skin and useful for larger wounds.
- Silicone mesh: Lightweight and non-sticky, it shields the wound while allowing airflow.
These alternatives provide relief for irritated skin while keeping wounds clean and protected.
Choosing the right one depends on the injury type and sensitivity level.
Tips for Preventing Skin Irritation From Medical Dressings
Why does something meant to help sometimes end up causing more discomfort? Medical dressings protect wounds but can irritate sensitive skin provided they are not applied carefully.
Proper skin care starts with cleaning the area gently before dressing application to remove dirt and bacteria. Choosing hypoallergenic options or barrier creams can reduce reactions. Avoid pulling adhesives too tight, as friction worsens irritation. Rotating dressing locations helps prevent constant pressure on one spot.
Checking the skin daily for redness or itching catches problems promptly. Letting the skin breathe between changes minimizes moisture buildup, a common irritant. For dry skin, moisturizing (away from open wounds) keeps it resilient.
Loose, breathable fabrics around dressings reduce rubbing. These small steps make a big difference in keeping skin comfortable while healing.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Allergy Symptoms
At what point does a minor reaction cross the line into needing professional help? Allergy severity varies, but certain signs demand a medical evaluation to avoid complications. Mild redness or itching might resolve on its own, but worsening symptoms shouldn’t be ignored.
- Persistent or spreading rash: Should irritation grow or last beyond a few days, it’s time to consult a doctor.
- Swelling or blistering: These indicate a stronger reaction, especially near the eyes, mouth, or throat.
- Difficulty breathing or dizziness: These severe symptoms require immediate attention.
- Fever or infection signs: Warmth, pus, or increased pain suggest a secondary infection needing treatment.
Recognizing the time to seek help guarantees safety and prevents minor issues from escalating.
Trusting instincts is key—should something feel off, professional advice is the best next step.
Conclusion
Even the slightest breeze against a Tegaderm allergy could send someone into a frenzy of itching so intense, they’d scratch their skin raw. But fear not—switching to hypoallergenic dressings could feel like trading sandpaper for silk. With options like silicone-based adhesives or gentle gauze, irritation becomes a distant memory. The right choice transforms healing from an itchy nightmare into smooth, soothing relief, where the biggest worry is deciding which blissfully irritation-free bandage to use next.