You may have noticed bumps on your skin and questioned whether they’re harmless Fordyce spots or something more concerning like herpes. It’s easy to confuse the two, particularly when you’re uncertain what to look for. Grasping their key differences can help put your mind at ease and guide you to the right approach for handling each condition. Let’s analyze what sets these skin irregularities apart, starting with how they appear and where they show up.
Overview of Fordyce Spots and Herpes
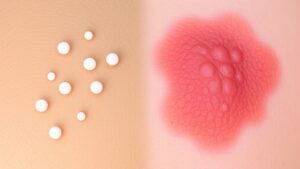
Should you notice bumps on your skin, it can be puzzling, especially provided that you’re trying to figure out whether they’re something harmless like Fordyce spots or a sign of something more concerning like herpes.
Fordyce spots are common, harmless small bumps caused by sebaceous glands, showing up as white or yellowish dots, usually 1–3 mm wide. They’re totally asymptomatic and don’t change over time.
On the other hand, herpes, which can be an STD, appears as painful, fluid-filled blisters that often cluster and can lead to sores.
While both might seem similar at initial glance, Fordyce spots are non-contagious and unrelated to infections, unlike genital herpes, which requires medical attention. Grasping this distinction is vital for your peace of mind.
Symptoms: How Fordyce Spots Differ From Herpes
At the time it comes to symptoms, Fordyce spots and herpes couldn’t be more different.
You’ll observe that Fordyce spots are small, painless bumps, while herpes gives you painful, fluid-filled blisters that can be a real nuisance.
Plus, unlike herpes, Fordyce spots don’t cause any itching or burning, so grasping these differences can really help you feel more at ease.
Pain and Discomfort Levels
Although you could observe some skin bumps that raise concerns about their nature, grasping the variations in pain and discomfort levels can provide you peace of mind.
Here’s how Fordyce spots differ from herpes lesions regarding sensations you could feel:
- Fordyce spots are typically painless and don’t cause any discomfort.
- Herpes lesions often produce burning, itching, or tenderness, making them quite uncomfortable.
- You could experience flu-like symptoms with herpes, while Fordyce spots never result in systemic symptoms.
Understanding these differences can help ease your worries.
Keep in mind, should you have persistent symptoms or concerns, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Appearance and Texture Differences
While you could fret over unusual bumps on your skin, comprehending the look and feel distinctions between Fordyce spots and herpes can provide some comfort. Fordyce spots are small, non-inflamed bumps that can be white or yellow and slightly raised. They appear similar to other skin conditions but remain flush with your skin and don’t ulcerate.
In contrast, herpes presents as fluid-filled blisters clustered on a red, inflamed base, often developing into painful cold sores that might burst. You won’t experience the tingling or burning sensations that accompany herpes outbreaks with Fordyce spots, and they don’t crust or scab during healing, maintaining a smooth texture over time.
Grasping these differences helps ease your worries.
Fluid Presence Absence
Grasping the distinction between Fordyce spots and herpes, particularly concerning fluid presence, can help put your mind at ease. Here’s what you need to know:
- Fordyce spots are solid, non-fluid-filled sebaceous (oil) glands and don’t ooze or weep.
- Herpes lesions, on the other hand, are fluid-filled and can rupture, leading to crusting.
- Before herpes blisters appear, you could feel tingling or itching, which doesn’t happen with Fordyce spots.
Appearance and Location Variations
At the moment you notice something unusual on your skin or lips, distinguishing between Fordyce spots and herpes can be reassuring and vital for your peace of mind. Fordyce spots appear as small, white, or yellowish bumps, often found as spots on your lips, cheeks, or genital area. These spots are the result of enlarged oil glands and tend to stay the same in size and number.
In contrast, herpes shows up as clusters of fluid-filled vesicles, typically on keratinized skin, and can experience changes in shape and size. Unlike Fordyce spots, herpes lesions often come with inflamed, red bases and can ulcerate, crust over, or coalesce, making careful observation pivotal for accurate identification.
Contagious Nature of Fordyce Spots vs. Herpes
In the context of the contagious nature of Fordyce spots and herpes, there’s a clear divide.
You’ll find that Fordyce spots aren’t contagious at all, while herpes is easily spread through skin contact and bodily fluids.
Grasping these differences can help ease concerns and clarify what precautions, whenever applicable, you may need to take.
Non-Contagious Fordyce Characteristics
While numerous individuals could fret about the contagious nature of skin conditions, it’s crucial to grasp that Fordyce spots are entirely harmless and non-contagious. These sebaceous glands, initially identified by John Addison Fordyce, are natural parts of your skin’s anatomy.
Here are some characteristics that reassure you:
- Benign nature: Fordyce spots are benign and pose no health risks.
- Stable appearance: Unlike herpes, these spots don’t change, swell, or cause pain.
- No treatment required: There’s no need to remove Fordyce spots, as they don’t disrupt your wellness.
Understanding that these spots are completely harmless will help you feel more at ease. So, no need to worry—they’re just a simple part of your skin’s terrain!
Herpes Transmission Pathways
Comprehending how different skin conditions spread can greatly assist in calming your thoughts. In instances involving herpes, you should know that it’s a sexually transmitted infection. It spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact or bodily fluids, making it contagious even in situations where you don’t see sores.
In contrast, Fordyce granules are harmless and non-contagious; they can’t spread sexually or through shared items like towels. Herpes also poses a transmission risk through asymptomatic shedding, meaning the virus can be passed even without visible symptoms.
Fordyce spots, however, have zero risk of transmission at any time. Identifying these differences can help you better manage your health concerns, and it’s perfectly normal to feel a little anxious about these topics.
Distinction in Infection Risks
Comprehending the distinctions in infection risks between Fordyce spots and herpes can offer you much-needed peace of mind. Recognizing these key differences can alleviate any concerns you might have:
- Fordyce Spots: These are harmless oil glands that aren’t contagious, meaning you can’t spread them to partners.
- Herpes: Caused by highly contagious HSV-1 or HSV-2 viruses, it transmits through skin-to-skin contact and poses an infection risk during outbreaks.
- Presence and Testing: Fordyce spots are present from birth and don’t appear in blood tests, while herpes antibodies can be detected, confirming an infection.
Being informed aids you in acknowledging that Fordyce spots are entirely non-threatening, enabling you to focus on your health without unnecessary anxiety.
Diagnostic Methods for Accurate Identification
Determining whether you’re handling Fordyce spots or herpes can occasionally seem puzzling. A healthcare provider typically conducts a visual inspection for identification. Fordyce spots show up as tiny, uniform white or yellowish papules, often without inflammation.
Should it be necessary, they’ll employ a dermatoscope to reveal the sebaceous gland structure of Fordyce spots, contrasting with herpes’s vesicular or ulcerated form. Diagnosing herpes often demands more sophisticated diagnostic methods, like PCR swabs or viral cultures from active lesions.
You might require a biopsy, although it’s rare; this can verify Fordyce spots via identifying ectopic sebaceous glands, while hsv displays multinucleated giant cells. Keep in mind, Tzanck smear tests aren’t useful for Fordyce spots but can indicate herpes infection through nuclear changes.
Treatment Options and Prognosis for Both Conditions
Grasping how to manage Fordyce spots and genital herpes can help ease some concerns. Here’s what you need to know about treatment and prognosis:
- Fordyce Spots: No medical treatment is necessary, but you can remove them using laser treatment or electrosurgery for cosmetic reasons. They won’t recur after removal.
- Genital Herpes: Antiviral medications like acyclovir are effective for managing outbreaks, but the virus remains dormant and could return periodically.
- Visibility Options: Topical retinoids can help reduce the appearance of Fordyce spots, while pain relievers can ease discomfort from herpes outbreaks.
Understanding these treatments can enable you to manage your health confidently and relieve some anxiety you could feel about either condition.