You may not contemplate them often, but your muscles are working hard every second—whether you’re lifting groceries, running for the bus, or just breathing. They’re more than just bundles of fibers; they’re the engines behind every move you make, and keeping them healthy means comprehending how they function, what they need, and how to care for them. Ready to uncover what makes your body’s powerhouses tick—and how to keep them strong for the long haul?
The Structure and Composition of Muscles
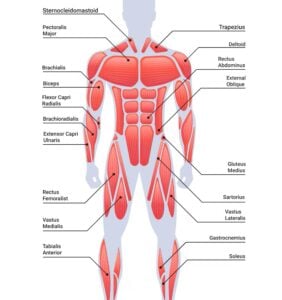
Muscles aren’t just what make you strong—they’re the concealed engines powering every move you make. Made up of thousands of intertwined muscle fibers, they form muscle tissue that makes nearly half your body weight.
These fibers bundle into fascicles, with each fiber wrapped in a sarcolemma, a membrane that helps communicate signals for movement. Inside, myofibrils packed with actin and myosin proteins slide past each other, shortening your muscles once you flex.
Calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum kicks off the process, acting like a switch for every contraction. Without this precise structure, you couldn’t lift a finger—literally.
Your muscles adapt, grow, and repair, keeping you moving effortlessly. Comprehending their composition helps you appreciate the complexity behind even the simplest actions.
Three Types of Muscle Tissue and Their Roles
While you could contemplate all muscles work the same way, your body actually relies on three distinct types—each with its own job.
Skeletal muscle, the kind you control, helps you move bones as you walk or lift. It’s striated and voluntary, meaning you decide at what point it contracts.
Cardiac muscle, found only in your heart, works nonstop without you realizing—it’s involuntary but also striated, pumping blood to keep you alive.
Smooth muscle lines organs like your stomach and blood vessels, assisting with digestion and blood flow. Unlike the others, it’s non-striated and involuntary.
These three types of muscle guarantee everything from your heartbeat to your digestion runs smoothly. Comprehending their roles helps you appreciate how your body stays active, even while you’re not consciously trying.
How Muscles Work Together for Movement
As you reach for a glass or take a step forward, your muscles don’t just act alone—they team up in precise, coordinated ways to make movement effortless.
Whenever muscles move, they work together like a well-trained team. Your biceps contract to bend your arm while your triceps relax to let it happen—one pair of many that keep you smooth and steady.
Synergist muscles pitch in to help with tricky tasks, like whenever your rotator cuff aids your deltoid to lift your arm.
Even the speed of muscle fibers plays a role: slow-twitch ones keep you going on long walks, while fast-twitch ones fire up for quick sprints.
Every motion relies on these partnerships, proving your body’s teamwork is what keeps you moving with ease.
Major Muscle Groups and Their Functions
Your body’s strength and movement depend on powerful teams of muscles, each group specialized for different tasks.
Skeletal muscles, like those in your arms and legs, work together to help you move. Your biceps and triceps control bending and straightening your elbows, making it easier to lift or push things. The quadriceps in your thighs power walking and jumping, while the hamstrings at the back help you bend your knees, like whenever you’re running or cycling.
Your core muscles—including the abs and obliques—keep you stable, supporting your spine and improving posture. These major muscle groups don’t just help you stay active; they’re essential for everyday tasks, from carrying groceries to playing sports.
Comprehending how they work helps you appreciate their role in keeping you strong and mobile.
Common Muscle Injuries and How to Prevent Them
Muscle injuries like strains or tendonitis can sneak up on you in case you’re not careful, especially at the time you push too hard or use poor form.
Spotting initial warning signs—like persistent pain or stiffness—helps you act before things get worse. Simple habits, like warming up properly and strengthening key muscle groups, go a long way in keeping you injury-free.
Types of Muscle Injuries
As one pushes their body too hard or moves the wrong way, muscle injuries can sneak up on them—whether it’s a mild strain from overstretching or a full tear that stops them in their tracks.
A muscle injury often starts small, like a Grade 1 strain with minor fiber tears, but can escalate to Grade 3, where the muscle ruptures completely. Connective tissue, like tendons, isn’t immune either—tendonitis flares up from repetitive motions, like swinging a racket or typing with poor wrist positioning.
Overuse injuries creep in as one skips warm-ups or uses bad form, stressing muscles unevenly. Even everyday actions, like lifting groceries with weak arms, can strain tissues should one not be conditioned.
The key? Listen to your body—it’ll tell you at what point to ease up.
Preventing Muscle Strains
While muscle injuries like strains can sideline you unexpectedly, the positive aspect is many are preventable with the right habits.
To avoid muscle strains, start with a proper warm-up—light cardio and dynamic stretches prep your muscles for activity. Gradually increase intensity to let your body adapt, reducing sudden stress.
Focus on technique; poor form strains muscles unnecessarily. Stay hydrated and eat balanced meals to support muscle health, as dehydration and poor nutrition weaken tissues.
Don’t skip rest days—overuse leads to fatigue and injury. Listen to your body; pushing through pain invites trouble.
Strengthening exercises build resilience, while flexibility routines keep muscles supple. Small, consistent steps protect your overall health and keep you moving smoothly.
Symptoms Needing Attention
Should you have ever pushed through a workout only to feel a sharp twinge or dull ache afterward, it’s your body’s way of saying something’s off.
Your muscle is responsible for movement, so as pain lingers, it signals strain or injury. Mild discomfort could indicate a Grade 1 strain, while severe weakness or popping sounds could mean a tear. Persistent stiffness or pain lasting over a week? Don’t ignore it—your overall health depends on addressing these red flags.
Repetitive motions, like gripping weights too hard or improper wrist positioning, can lead to tendonitis (think tennis elbow).
Warm up properly, stretch regularly, and ease into new routines to prevent trouble.
Listen to your body—it knows the right time to slow down.
Signs of Muscle Strain and When to Seek Help
You may notice sharp pain or swelling in a muscle after overworking it—that’s a sign of strain.
Should the discomfort doesn’t fade in a few days or gets worse, it’s time to see a doctor. Ignoring severe symptoms can lead to bigger problems, so don’t push through the pain.
Recognizing Muscle Strain Symptoms
A sharp twinge or sudden ache could be your initial clue that something’s off—muscle strains sneak up when fibers stretch or tear from overuse or sudden movement.
Since muscles are made of bundles of fibers, even small tears cause pain, swelling, or bruising. You may notice stiffness, tenderness, or weakness in the affected area, making simple movements harder.
Mild muscle strain symptoms include soreness, while severe strains bring sharp pain, visible swelling, or even muscle spasms.
Should lifting your arm or walking feel unusually tough, that’s your body signaling damage. Listen to it—strained muscles need rest to heal.
Redness or warmth around the injury? That’s inflammation doing its job, but don’t ignore worsening pain.
Pay attention to these signs—knowing them helps you act fast.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice
Since muscle strains can range from mild discomfort to serious tears, grasping the right time to seek help prevents long-term damage. Your muscular system is crucial for movement and overall health, so ignoring severe symptoms risks worsening the injury. Should pain linger beyond a week, movement becomes impossible, or swelling and bruising appear, see a doctor. Chronic pain could signal deeper issues needing treatment.
| Symptom | Possible Grade | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Mild pain | Grade 1 | Rest, ice, monitor |
| Weakness | Grade 2 | Limit activity, consult if worsens |
| Severe swelling | Grade 3 | Seek immediate care |
| Unexplained pain | N/A | Get evaluated for fundamental causes |
Listen to your body—early care keeps you active and healthy.
Essential Exercises for Muscle Strength and Flexibility
Building muscle strength and flexibility doesn’t have to feel overwhelming—just a few key exercises can make a big difference.
Whether you’re new to strength training or looking to improve flexibility, these moves will help you build a balanced routine.
- Squats: Strengthen your legs and core while boosting flexibility in your hips and knees. Keep your back straight and lower slowly.
- Lunges: Work your quads, hamstrings, and glutes while improving balance and mobility. Step forward, bend both knees, and push back up.
- Hamstring Stretch: Sit and reach for your toes to loosen tight muscles. Hold for 20-30 seconds to improve flexibility.
- Push-Ups: Build upper-body strength while engaging your core. Modify by dropping to your knees if needed.
Focus on form, breathe deeply, and progress gradually for the best results.
The Role of Nutrition in Muscle Health
Your muscles need the right nutrients to stay strong and healthy, so let’s talk about what keeps them working at their best.
Protein helps repair and build muscle, while carbs fuel your workouts and fats reduce soreness.
Staying hydrated also keeps your muscles performing well and speeds up recovery whenever you push them hard.
Essential Nutrients for Muscles
Three key nutrients—protein, carbs, and fats—work together to keep your muscles strong and energized. Without them, your muscles can’t repair, grow, or perform at their best. Here’s how each one helps:
- Protein: Builds and repairs muscle tissue. Aim for 1.2–2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight daily, especially after workouts.
- Carbs: Fuel your muscles during exercise. Active individuals need 3–7 grams per kilogram to maintain energy levels.
- Healthy fats: Reduce inflammation and support recovery. Omega-3s from fish or flaxseeds are especially helpful.
- Vitamins & minerals: Magnesium, calcium, and vitamin D guarantee proper muscle function and prevent cramps.
Balance these nutrients to keep your muscles working smoothly. Skip one, and you may feel weaker or slower.
Your body thrives once you give it what it needs!
Hydration and Muscle Function
Just as the right nutrients fuel your muscles, staying hydrated keeps them working smoothly. Water makes up about 75% of your muscle tissue, so even mild dehydration can weaken contractions and leave you feeling sluggish.
Before exercise, drink 17-20 ounces of water a few hours ahead, then another 8 ounces right before to stay sharp. Electrolytes like sodium and potassium also matter—they help muscles contract and balance fluids, especially during long workouts.
Good hydration boosts blood flow, delivering nutrients and clearing waste so your muscles recover faster. Sip water throughout the day, not just during activity, to support overall health.
Listen to your body—thirst or dark urine means you’re behind. Keep a bottle handy, and your muscles will thank you.
Muscle Recovery and Maintenance Tips
Since muscles work hard during exercise, giving them time to recover properly is key to avoiding injury and staying strong.
Proper muscle recovery supports overall health by helping one bounce back faster and perform better. Here’s how to take care of your muscles:
- Rest and sleep: Your muscles repair themselves during rest, so aim for 7-9 hours of sleep nightly.
- Hydrate and nourish: Drink water and eat protein-rich foods to rebuild muscle fibers and replenish energy.
- Stretch and move: Gentle stretching or light activity (like walking) eases soreness and boosts blood flow.
- Use the RICE method: Should you be injured, rest, ice, compress, and elevate to reduce swelling and pain.
Listen to your body—pushing too hard slows recovery. Small steps now keep you stronger later.
Key Takeaways for Optimal Muscle Function
To keep your muscles working at their best, it’s essential to understand how they function and what they need. Your muscles use energy to move, support your posture, and even regulate body temperature, so fueling them with balanced nutrition and hydration is key.
Warm up before activity to prep slow and fast-twitch fibers, and cool down afterward to prevent stiffness. Listen to your body—overworking leads to strains, so rest as necessary. Stretch regularly to maintain flexibility and avoid injuries like tendonitis.
Keep in mind, neutral wrist positioning and a relaxed grip reduce strain during workouts. Strong muscles boost overall health by improving metabolism and circulation.
Prioritize recovery with the RICE method in case you’re sore. Small habits add up to big benefits!